How to Differentiate Between Kidney Stones vs UTI: Key Factors and Diagnostic Tips
How to Differentiate Between Kidney Stones vs UTI: Key Factors and Diagnostic Tips
Blog Article
Exploring the Effects and Causes of Kidney Stones in Comparison to Urinary System Infections: A Detailed Guide
The expedition of kidney stones and urinary system infections (UTIs) reveals a complicated interaction of symptoms and underlying causes that call for mindful evaluation. While both problems can bring about hematuria, they present unique professional features and occur from various etiological variables. Understanding the nuances of each problem is critical for effective diagnosis and administration. What are the crucial distinctions in their symptoms, and how might these notify treatment methods? The solution to these inquiries may provide important insights into the avoidance and treatment of these typical urological concerns.
Review of Kidney Stones
Kidney rocks, likewise understood as renal calculi, type when certain substances in the urine crystallize and accumulation, bring about the growth of tough down payments within the kidneys. These rocks can differ in size, varying from a grain of sand to a golf sphere, and can be composed of different materials, the most common being calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine. The formation of kidney rocks is affected by a number of elements, including nutritional routines, fluid intake, and hereditary proneness.
Signs of kidney stones may consist of serious pain in the back or side, blood in the pee, nausea or vomiting, and regular urination, specifically as the rock moves via the urinary system system. Diagnosis generally involves imaging researches such as ultrasound or CT scans, together with urinalysis to identify the rock's structure.
Treatment alternatives vary based upon the size and kind of rock, as well as the extent of signs (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Small rocks may pass normally with enhanced liquid intake, while bigger stones might need clinical interventions such as lithotripsy or medical removal. Recognizing the pathophysiology and danger factors linked with kidney stones is crucial for efficient avoidance and management
Review of Urinary System Infections
Urinary system infections (UTIs) are usual microbial infections that affect any part of the urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. They mostly take place when bacteria, frequently from the intestinal system, get in the urinary system, leading to swelling and infection.
The frequency of UTIs is notably higher in women than men, mainly because of anatomical differences, such as a shorter urethra. Danger aspects consist of sex, specific contraceptive techniques, urinary system retention, and dehydration. The medical diagnosis of UTIs is normally verified with pee tests, which may expose the existence of germs, white blood cells, or red blood cells.
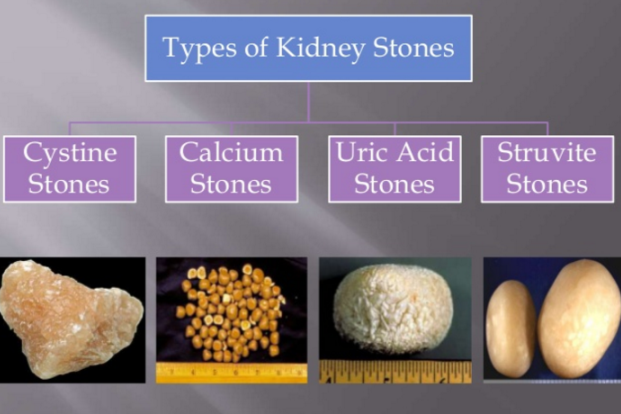
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
The pain connected with kidney stones can manifest in numerous methods, typically leading individuals to look for clinical interest. Among one of the most typical signs and symptoms is extreme discomfort, usually localized in the reduced back or side, which may radiate to the abdominal area or groin. This pain, often defined as sharp or cramping, can happen all of a sudden and might change in intensity.
In addition, individuals might experience hematuria, or blood in the urine, which can range from tiny total up to noticeable discoloration. This signs and symptom may be gone along with by changes in urinary system practices, such as increased regularity or urgency, in addition to discomfort throughout urination. Queasiness and throwing up are likewise prevalent, commonly arising from the body's response to extreme discomfort.
Sometimes, individuals might experience high temperature and chills, especially if a second infection develops because of the blockage caused by the stones. Generally, the mix of severe pain, hematuria, modified urinary system patterns, and stomach symptoms can supply substantial understanding into the presence of go kidney stones, calling for punctual clinical evaluation and intervention. Comprehending these signs is critical for timely diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
Signs of Urinary System System Infections
Infections within the urinary system system commonly offer a series of distinctive symptoms that can significantly impact every day life. The most common symptoms include a persistent urge to urinate, frequently accompanied by a burning sensation during peeing, recognized as dysuria. People might likewise experience boosted frequency of urination, producing percentages of pee each time.
Various other significant signs include cloudy or foul-smelling pee, which may indicate the presence of microorganisms or pus. In many cases, pee may show up pink or red because of the presence of blood, a condition recognized as hematuria. Furthermore, individuals may experience pelvic pain or pressure, which can have a peek at this site further exacerbate the sensation of seriousness.
Systemic symptoms might additionally materialize, such as fever, cools, and tiredness, especially if the infection has actually risen to the kidneys. It is vital to recognize these signs and symptoms early, as without treatment urinary system infections can cause more extreme issues. Kidney Stones vs UTI. Prompt clinical attention is suggested when these signs are observed, enabling proper diagnostic analysis and treatment to relieve discomfort and protect against additional health problems
Causes of Each Problem
Regularly, kidney stones and urinary system infections emerge from distinct yet in some cases overlapping reasons that can influence people differently. Dehydration, inadequate liquid consumption, and high-sodium diet regimens can exacerbate these conditions, promoting condensation within the urinary system system.
Understanding these distinctive reasons is vital for avoidance and treatment. Kidney Stones vs UTI. While lifestyle modifications might alleviate the danger of kidney stones, appropriate health and timely treatment of urinary system system infections are vital for decreasing click here for info their recurrence and linked difficulties
Final Thought
In summary, kidney rocks and urinary system tract infections existing distinct signs and underlying reasons. Kidney stones are identified by severe pain and metabolic variables, while urinary system infections primarily include microbial infections leading to urinary system seriousness and pain.
The expedition of kidney stones and urinary system system infections (UTIs) reveals a complicated interaction of symptoms and underlying causes that call for mindful evaluation.Urinary system system infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that impact any kind of part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.Often, kidney rocks and urinary system system infections arise from unique yet occasionally overlapping reasons that can affect individuals in a different way.In recap, kidney rocks and urinary system system infections present distinct signs and underlying reasons. Kidney rocks are identified by extreme discomfort and metabolic factors, while urinary tract infections mainly include microbial infections leading to urinary system seriousness and pain.
Report this page